
Oct 24, 2024 | Blog, Immigrate to Canada, Immigration, In the News, New Immigration Programs, Student Visas, Temporary Foreign Workers, Where to seek help
Immigration, Refugees, and Citizenship Canada (IRCC) unveils the 2025-2027 Immigration Levels Plan. This plan outlines the target number of permanent residents Canada will accept annually over the next three years. The plan significantly impacts Canada’s population growth, influencing social systems, taxation, housing, healthcare, and labor market expansion.
This year’s plan marks a significant shift, for the first time, the upcoming plan will include temporary residents, such as work permit holders, international students, and visitor visa holders. This marks a departure from previous years, when the plan focused solely on permanent residents.
In 2023, temporary residents accounted for 6.2% of Canada’s population. The government aims to reduce this percentage to 5% over the next three years.
The primary goal of the plan is to reduce the number of temporary residents in Canada to 5% of the total population by 2026. This reduction is aimed at achieving sustainable population growth and ensuring the country’s long-term economic prosperity.
To achieve this goal, the government has implemented several strategies. First, it has decreased the overall number of permanent resident admissions for the next three years. Second, the plan prioritizes in-Canada applicants, recognizing that newcomers with prior Canadian experience are more likely to integrate successfully and contribute to the economy.
Furthermore, the plan emphasizes economic immigration, allocating approximately 62% of permanent resident admissions to economic streams. This is intended to help address labor shortages in key sectors such as healthcare and trades. While the plan reduces permanent resident targets, it also maintains family reunification and refugee resettlement.
In addition to these measures, the government has introduced reforms to the Temporary Foreign Worker Program and the International Student Program. These reforms aim to limit the number of temporary residents entering Canada and ensure that those who do come contribute positively to the country.
News release
The 2025–2027 Immigration Levels Plan is expected to result in a marginal population decline of 0.2% in both 2025 and 2026 before returning to a population growth of 0.8% in 2027. These forecasts account for today’s announcement of reduced targets across multiple immigration streams over the next two years, as well as expected temporary resident outflows resulting from the 5% target, natural population loss and other factors.
Compared to last year’s plan, the Canadian Government is:
- reducing from 500,000 permanent residents to 395,000 in 2025
- reducing from 500,000 permanent residents to 380,000 in 2026
- setting a target of 365,000 permanent residents in 2027
The Levels Plan also supports efforts to reduce temporary resident volumes to 5% of Canada’s population by the end of 2026. Given temporary resident reduction measures announced in September and this past year, Canada’s temporary population will decrease over the next few years as significantly more temporary residents will transition to being permanent residents or leave Canada compared to new ones arriving.
Specifically, compared to each previous year, we will see Canada’s temporary population decline by
- 445,901 in 2025
- 445,662 in 2026
- a modest increase of 17,439 in 2027
Quick Facts
- Canada’s population has grown in recent years, reaching 41 million in April 2024. Immigration accounted for almost 98% of this growth in 2023, 60% of which can be attributed to temporary residents.
- This plan to right-size population growth after the post-pandemic surge will support continued robust GDP growth and enable GDP per capita growth to accelerate throughout 2025 to 2027, as well as improve housing affordability and lower the unemployment rate.
- Reducing the volume of immigrants will help to alleviate some pressure in the housing market, with the housing supply gap expected to decrease by approximately 670 000 units by the end of 2027.
- The temporary resident targets in the levels plan do not include short-term visitors or seasonal workers, who are not captured in annual population estimates. Targets are for the number of net new temporary residents entering Canada each year.
- The Government of Canada has put in place measures to manage the volume of temporary resident arrivals, uphold the integrity of our immigration system and protect vulnerable people, including
According to Statistics Canada, immigrants are making important contributions across every sector of Canada’s economy—namely, health care, construction and transportation. When it comes to Canada’s residential construction sector, immigrants play a key role, accounting for 23% of all general contractors and residential builders.
Other measures from the 2025-2027 Immigration Levels Plan
- Transitioning more temporary residents who are already in Canada as students and workers to permanent residentsRepresenting more than 40% of overall permanent resident admissions in 2025, these residents are skilled, educated and integrated into Canadian society. They will continue to support the workforce and economy without placing additional demands on our social services because they are already established, with housing and employment.
- Focusing on long-term economic growth and key labour market sectors, such as health and tradesPermanent resident admissions in the economic class will reach 61.7% of total admissions by 2027.
- Strengthening Francophone communities outside Quebec and supporting their economic prosperityOf the overall permanent resident admission targets, Francophone immigration will represent
- 8.5% in 2025
- 9.5% in 2026
- 10% in 2027
A recap of the recent immigration changes in canada
Study Permits
IRCC has imposed a cap on the number of study permits it will process for international students. This year, the department expects to process 606,000 applications, with an anticipated approval rate of 360,000. This represents a 35% reduction compared to 2023.
This decision surprised many, given the minister’s previous stance against setting caps or targets for Canada’s international student program. International students constituted 42% of Canada’s temporary residents in 2023.
Moreover, IRCC plans to further reduce the number of study permits processed in 2025 to 437,000. Notably, master’s and PhD students, previously exempt, will now be included under the cap.
Open Work Permits
IRCC also intends to decrease the number of Post-Graduation Work Permits (PGWPs) and Spousal Open Work Permits (SOWPs) issued over the next three years.
New eligibility requirements have been introduced for PGWP applicants. They must now demonstrate a Canadian Language Benchmark (CLB) score of at least 7 if they are university graduates or CLB 5 if they are college graduates. These changes are expected to result in 175,000 fewer PGWPs being issued over the next three years.
Changes to the SOWP program will also reduce the number of temporary residents. Spouses of international master’s students may now only be eligible for a SOWP if their spouse’s program is 16 months or longer or if they are enrolled in a program deemed critical or in-demand.
Spouses of “highly skilled, specialized workers” will remain eligible for SOWPs. However, stricter criteria will likely lead to a reduction of 100,000 open work permits over the next three years.
Overall, IRCC expects to issue 325,000 fewer open work permits in the coming years.
Closed Work Permits
The Temporary Foreign Worker Program (TFWP) has also undergone changes. Employers can no longer hire more than 10% of their total workforce through the TFWP. Additionally, the maximum duration of employment for workers hired through the Low-Wage stream has been reduced from two years to one year.
IRCC will not process low-wage Labour Market Impact Assessments (LMIAs) from employers in Census Metropolitan Areas (CMAs) with an unemployment rate higher than 6%, with certain exceptions. While the minister did not provide an estimate, these changes are expected to reduce the number of temporary foreign workers in Canada.
Permanent Residents
The Immigration Levels Plan 2024-2026 set a target of welcoming 500,000 permanent residents annually in 2025 and 2026.
Permanent residents can be admitted through economic immigration, family class sponsorship, refugee and protected persons, and humanitarian lines of business.
Minister Miller has stated that all options are on the table regarding the number of permanent residents Canada will admit in the coming years and that changes would be significant. He has indicated a potential shift in the “type of immigration Canada is supporting.”
Currently, 60% of immigration to Canada focuses on economic immigrants. The minister has suggested that this level may be reconsidered.
Factors Influencing the Plan
The increasing population has raised concerns among Canadians about the impact on affordable housing and healthcare. These issues are expected to influence the next federal election and were highlighted in the 2023 Environics Institute report on Canadian support for immigration.
The report noted a decline in support for immigration among Canadians compared to previous years. Many Canadians expressed concerns about the projected high level of immigration and its potential strain on resources.
Minister Miller has also emphasized the need to address the number of temporary residents, particularly international students, to prevent fraud and ensure adequate support for newcomers.
Despite these concerns, both Miller and Boissonnault have consistently highlighted the cultural advantages of immigration and its contribution to Canada’s labor force growth. They have stressed the importance of finding a balanced approach.
Are you affected by these measurements?
If you’re affected by these changes to the immigration programs, seeking professional guidance is crucial. Our experienced immigration experts can provide tailored advice to help you navigate the new regulations and understand your options. Whether you’re a foreign worker looking to continue your employment in Canada or an employer seeking to hire temporary foreign workers, our team can assist you in finding the best solutions and staying informed about the latest updates. Get assistance here.
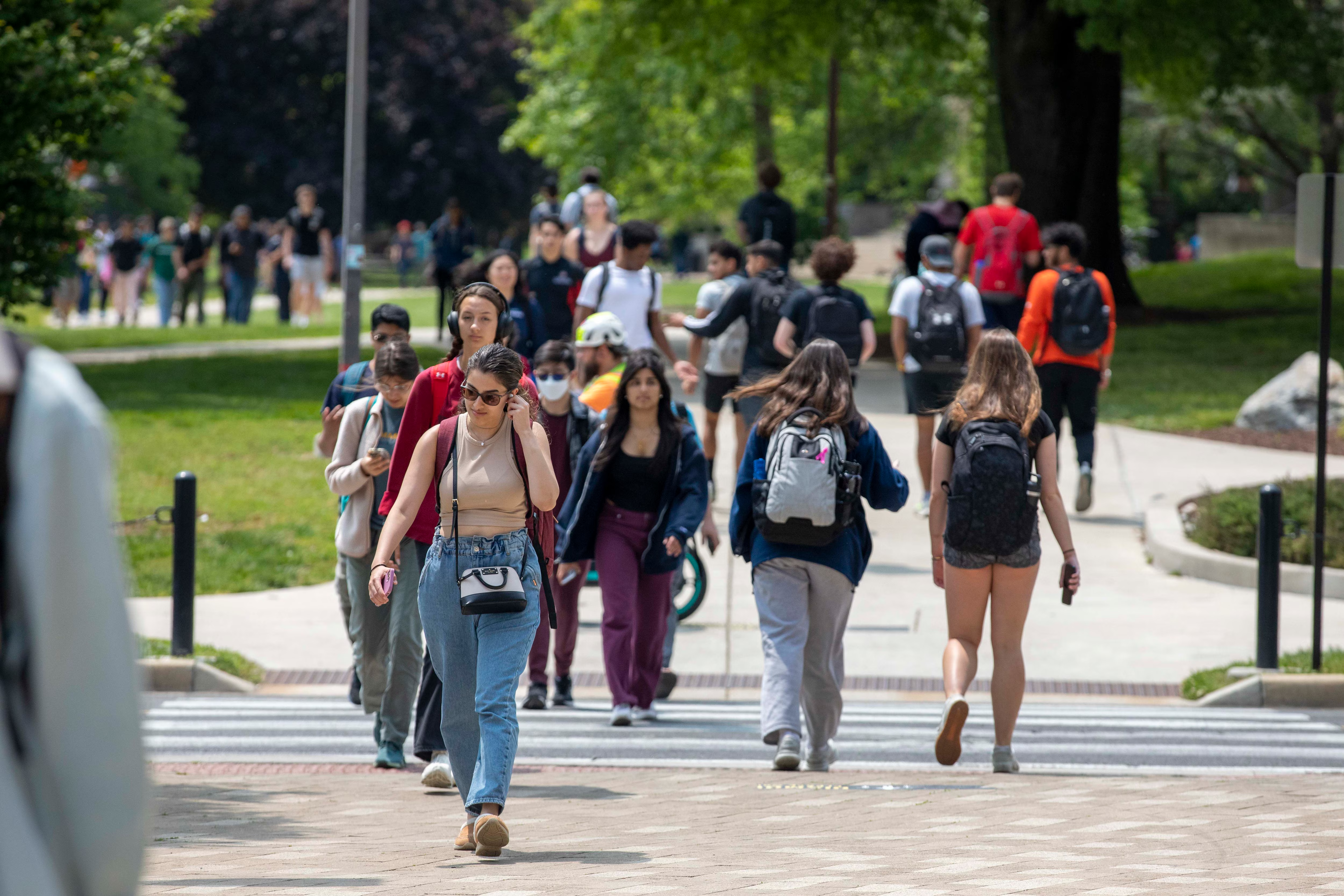
Jul 10, 2024 | Blog, Immigrate to Canada, In the News, Student Visas, Where to seek help
Canada is set to halt processing study permits for colleges and universities that do not monitor international students’ enrollment, according to new government plans.
Under the proposed regulations, post-secondary institutions must inform the federal Immigration Department about whether international students are attending classes and complying with study permit conditions.
This initiative aims to bolster confidence in Canada’s international student program. As outlined in the Canada Gazette, students will need to obtain a new study permit each time they switch schools or start a new program.
Federal Oversight and Provincial Jurisdiction
While the federal government is taking steps to enforce these measures, it must navigate the fact that educational governance falls under provincial jurisdiction.
The Immigration Department oversees the entry of international students and sets conditions for study permit holders while in Canada. It also decides whether to issue study permits, although provinces designate which institutions can admit international students.
Federal officials have faced challenges in monitoring students post-entry, including verifying enrollment and compliance before permit extensions or post-graduation work permits are considered.
Integrity Measures and Program Expansion
“The amendments in question are designed to enable IRCC (Immigration, Refugees and Citizenship Canada) to effectively address integrity issues and combat instances of unethical conduct that undermine program integrity,” stated a recent government notice released for public feedback.
Canada saw a significant rise in study permit holders, welcoming over one million in 2023, up from 352,305 in 2015.
The rapidly expanding international student program has garnered attention due to aggressive recruitment by post-secondary institutions and unregulated foreign agents. Many migrants view studying in Canada as a pathway to work and eventually obtain permanent residency.
Policy Adjustments and Proposed Framework
International students have faced blame for Canada’s housing shortages, healthcare demands, and social tensions. In response, Immigration Minister Marc Miller has proposed a two-year limit on new study permits issued.
These proposed adjustments are part of a strategy to implement a “trusted institution framework” this autumn. The framework aims to evaluate designated learning institutions and expedite study permit processing for institutions deemed “trusted,” encouraging responsible student admissions within the sector.
Financial Implications and Off-Campus Work Hours
The projected expenses over the next decade are anticipated to total nearly $87 million in present value, encompassing government implementation costs, expenses for designated learning institutions, and fees for study permit holders seeking to transfer schools.
Additionally, the regulatory revisions propose an increase in the maximum weekly off-campus work hours for international students from 20 to 24 hours, as previously outlined by Miller. This adjustment is aimed at assisting international students in managing rising living expenses, as indicated by government sources
Interested parties are invited to provide feedback on the proposed amendments until July 29.

Sep 6, 2023 | Blog, Immigration, In the News, New Immigration Programs, New Laws, Student Visas
Canada is a popular destination for international students, with over 600,000 foreign students enrolled in the country each year. However, Canada’s international student program has been criticized for its lack of transparency and oversight. In response to these concerns, the Canadian government launched the Trusted Institutions Framework (TIF) in 2023.
Canada Trusted Institutions Framework requirements
The TIF sets out a clear set of standards for institutions that want to be designated as “trusted institutions.” These standards cover three key areas:
- Compliance with Canadian laws and regulations: Institutions must have a history of complying with all applicable Canadian laws and regulations, including those governing immigration, education, and labour.
- Quality educational offering: Institutions must provide a quality educational offering that meets the standards of Canadian post-secondary education. This includes having qualified faculty, providing a rigorous curriculum, and offering a safe and supportive learning environment.
- Commitment to the safety and well-being of international students: Institutions must have a commitment to the safety and well-being of their international students. This includes providing support services such as counseling, translation, and immigration advice.
In addition to the three key requirements mentioned above, the TIF also includes a number of other provisions, such as:
- A requirement for institutions to have a risk management plan in place to address potential issues such as fraud and exploitation.
- A requirement for institutions to provide regular updates to the government on their compliance with the TIF.
- A mechanism for the government to revoke the designation of an institution that fails to meet the requirements of the TIF.
According to IRCC, “Given that these discussions are ongoing, IRCC cannot speculate on future policy decisions. However, any new developments would be communicated publicly.”
DLIs will be tasked with sharing additional data, including retention rates, on-time program completion, revenue from international tuitions, support services expenditure, housing availability, and teacher-student ratios.
Measuring Institutional Performance under the TIF
The Trusted Institutions Framework (TIF) will evaluate the performance of Designated Learning Institutions (DLIs) based on a number of key indicators, including:
- Retention rate: The percentage of international students enrolled in multi-year study programs who choose to continue their studies at the same institution after their first year in Canada.
- On-time program completion rate: The percentage of international students who complete their programs within the advertised length of study.
- Revenue from international tuition: The percentage of a DLI’s total tuition revenue that is derived from international student tuition fees.
- Scholarships for less developed countries: The dollar value and the percentage of total scholarships and grants awarded to international students from countries identified on the United Nations Least Developed Countries list.
- Funding for international student support: The value of dedicated support services provided to international students per student and as a percentage of average international student tuition.
- DLI-administered housing availability: The total number and percentage of international students who are accommodated in housing administered by their respective institutions.
- Teacher-student ratio: The average teacher-student ratio for the ten courses with the highest enrollment of international students.
These indicators will be used to assess the effectiveness and commitment of DLIs to providing a high-quality education and support services to international students.
Benefits of the Trusted Institutions Framework
Institutions that meet these requirements will benefit from a number of advantages, including:
- Priority access to Canadian immigration programs
- Recognition of their commitment to excellence
- Improved reputation
The TIF is still a new initiative, but it has the potential to make a significant difference in the lives of international students in Canada. By ensuring that institutions are held accountable to high standards, the TIF can help to create a more welcoming and supportive environment for international students.
Conclusion
The TIF is a significant step forward in improving the quality and safety of Canada’s international student program. By establishing clear standards for institutions and holding them accountable to those standards, the TIF can help to ensure that international students have a positive experience in Canada.
(more…)






 Useful Resources for Canada
Useful Resources for Canada
 Useful Resources for U.S.
Useful Resources for U.S.
 Our Local Immigration Services
Our Local Immigration Services